 content-marketing
content-marketing 
In the modern environment, a great deal of effort is being put into finding better, greater efficient, and more inexpensive ways to generate power. Giant corporations have often used gas turbines to generate power since 1939.
Gas turbines are among the most common power generation systems globally. However, they are still getting upgraded to offer uninterrupted power to communities across the world. This article will help you know how these gas turbine power plants operate to generate energy.
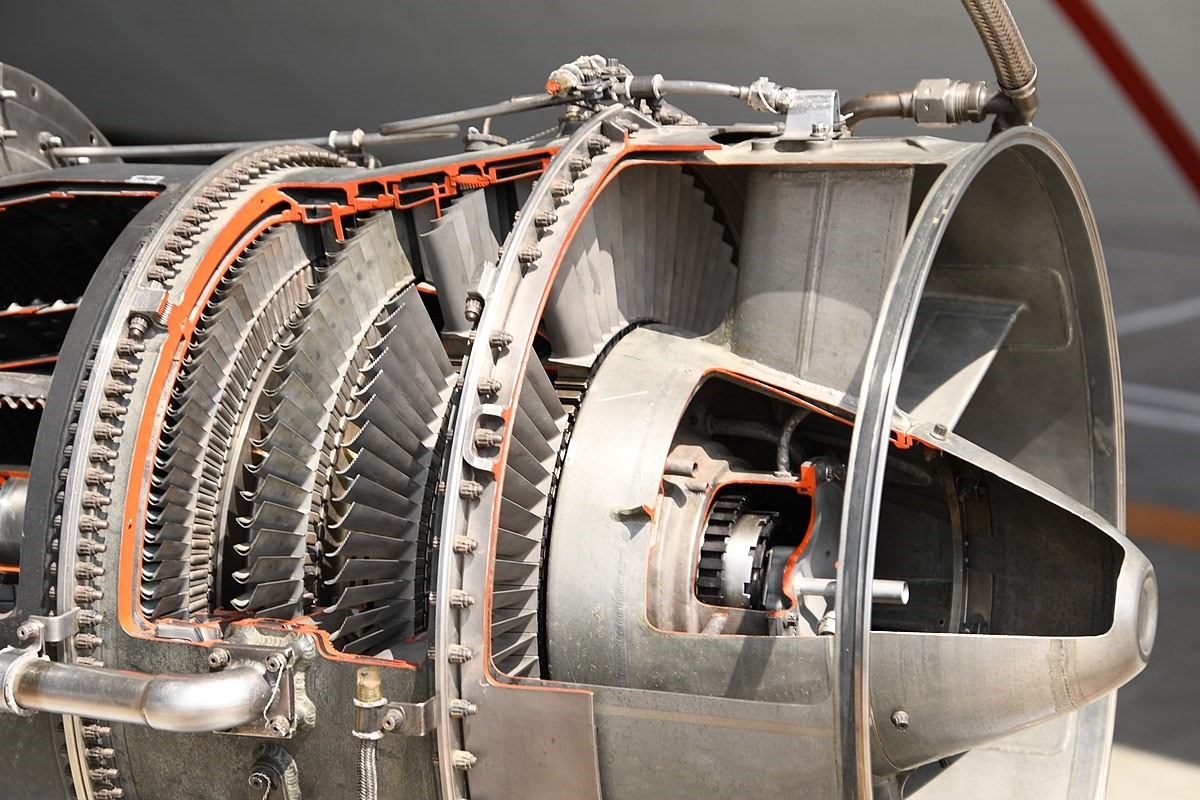
What are Gas Turbines?
Gas turbines are a type of internal combustion engine. In gas turbines, hot gases are produced by the ignition of an air-fuel mixture. Then, it uses these hot gases to spin a turbine to generate electricity. Gas turbines get their name from the generation of hot gas during fuel burning.
It uses fuel oils, natural gas, and synthetic fuels to produce energy. In gas turbines, the burning process continues, unlike in conventional Internal Combustion engines, where combustion occurs intermittently.
Gas Turbine Power Plant Benefits
Along with generating electricity, gas turbine services have several other advantages. Here are some of the best benefits of Gas Turbine Services to acknowledge:
Necessary Elements of a Gas Turbine Power Plant
Even though a gas turbine’s functions are intricate, it comprises three key components:
The compressor pumps air into the motor. The air is then compressed and supplied into the combustion process at speeds of hundreds of miles an hour. Then, the combustion system injects natural gas into the combustion chamber using fuel injectors. Due to the injection, it exceeds the temperatures up to 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit.
Eventually, the combusting gases enter the turbine, where it spins revolving blades. This blade rotates a generator that generates power for various energy marketplaces. This operation also draws additional air into the turbine, renewing the procedures.
Different Types of Gas Turbines and Their Elements
There are two main types of gas turbines power plants:
Elements: Starting motor, Compressor, Gas Turbine, Combustion Chamber, and Generator
Elements: Starting motor, Air heater, Air compressor, turbine, Heat Exchanger, and Generator.
How Does the Gas Turbine Power Plants Operate?
Check out the working procedures of gas turbine power plants. Both types have their own set of working methods. Let’s understand both processes from the following steps.
Working Procedure of Open Cycle
It subsequently converts the rotational mechanical energy into electrical energy through the generator. For example, an open cycle gas turbine generates electricity in this manner.
Working Procedure of Close Cycle
The close cycle gas turbine power plant operating in the following manner:
Conclusion
Here, we come to the end of the article. We hope this article offers all the necessary information you were looking for. From the advantages to types to elements, we have mentioned every accurate detail. Most importantly, you will get to learn the operating procedures of the gas turbines. Read the complete article to understand everything regarding the Gas Turbine Power Plants.