
 technology
technology 
[ad_1]
In 2021, consumers and institutions alike are fast-tracking a digital revolution in an unprecedented era of social distancing and remote work—a trend that may continue long after the pandemic subsides.
The time is ripe for many commercialized products and services to ride the wave of unparalleled high-speed connectivity and minimal latency enabled by 5G. Yet, the technology at the forefront of them all is without a doubt the smartphone. By combining mobile telephone and computing functions within a singular multi-purpose device, smartphones have brought about a profound scale of mobility and accessibility with one-stop services that empower consumers across every aspect of their daily lives.
Some may look back fondly on the good old days of the mobile phone, when voice calls and text messaging were all we had access to, in the absence of addictive social media platforms and the seemingly endless barrage of notifications we receive nowadays. Nonetheless, the instantaneous connectivity of ever-improving mobile networks and increasingly diverse applications of smartphones will undeniably continue to bring value to users.
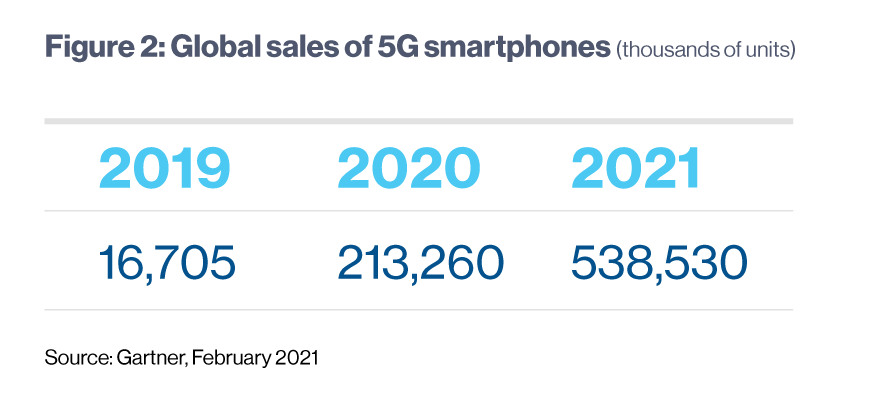
According to a forecast by vivo, one of the leading smartphone makers, demand for 5G devices is catching up to the entirety of the smartphone market as researchers recorded exponential growth between 2020 and 2021.
Another report, published by Gartner, showed that the worldwide demand for smartphones with 5G capabilities more than doubled this year. “In 2020, consumers reduced spending on smartphones, but the availability of new products will see users drive significant uptick in demand in 2021. Lower-end 5G smartphones, which are becoming more prevalent outside China, are poised to drive more momentum for 5G smartphones in 2021 across all regions,” said Anshul Gupta, senior research director at Gartner.
How did we get to where we are today, and how did smartphone brands take us here?
5G is the latest global wireless standard, otherwise known as the 5th generation of cellular mobile communication technology. Compared to 4G LTE technology, 5G increases flux density a hundredfold and connection density tenfold. This allows for a new kind of digital infrastructure that can connect virtually everything and everyone via peak data transmission speeds with minimal latency to provide a uniform experience to us all, culminating in higher efficiency and optimized performance to empower new user experiences.
Hundreds of thousands of industries are becoming integrated, owing to the reliable and streamlined network between machines, devices, and other digital objects. With many creative applications ranging from augmented reality/virtual reality experiences to vehicle-to-everything driverless cars and many more, 5G will provide humankind with the foundation to establish smart cities with comprehensive internet-of-things technologies that can efficiently restructure our lived environments and redefine our everyday lifestyles.
It goes without saying that 5G can facilitate limitless applications, on both industrial and consumer levels. For tech-savvy individuals accustomed to heavy device usage loads, 5G will be game-changing by elevating their collective digital devices into powerful, cloud-synced gateways capable of tapping into the most resource-intensive applications and data streams. Many industries are currently undergoing paradigm shifts as enterprises and countries race to propel society into the next phase of technological transformation.
The 5G technical standard was formed by a series of innovative R&D efforts led by companies such as vivo. The 5G products or services consumers are presented with today are actually a refined conglomeration of technologies formulated by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), a consortium of international telecom standards organizations that provide a stable platform for collaboration.
As the entire world becomes familiar with the limitless possibilities of contemporary mobile communications technology, consumers are looking to arm themselves with devices that contain cutting-edge capabilities in order to complement their connected and fast-paced daily lifestyles.
Corporations and governments are both racing to gear up in preparation for the new digital gold rush. Unbeknownst to many, battles are fought and alliances are formed every day as companies cannibalize each other in the race to hold the most patents for 5G technologies.
Vivo, one of the top players, has participated in the 3GPP 5G standard formulation for over five years. As one of many companies that set their sights on 5G technology, vivo established special 5G task forces back in December 2016 across Beijing and Shenzhen, China. One month later, vivo made its debut at the 2017 3GPP meeting. Since then, vivo has submitted over 5,000 5G proposals to the 3GPP, leading to 15 technical features and getting three technical projects approved. With more than 100 global standard experts staffed at its communication research institute, vivo now holds over 3,000 patents for 5G inventions.
As a leading smartphone company with in-depth R&D capabilities, vivo is dedicated to accelerating the empowerment of consumers en masse in this new era by designing cutting-edge 5G smartphones that are available at every price point. Having amassed over 400 million users worldwide, vivo has a deep understanding of evolving consumer demands and strives to bridge users with the digital world by becoming one of the leading contributors to 5G technology in the industry.
“The main gateway for consumers to indulge in the new digital era must be the most accessible, portable, cost-effective, and readily available digital device of them all: the smartphone. A leader in both smartphone manufacturing and 5G connectivity, vivo has been designing a diverse lineup of products that are ready for the next generation of connectivity to bring joy to users worldwide at modest price points,” says Rakesh Tamrakar, 5G standards expert at vivo.
Tamrakar has 20 years of experience in the mobile communications industry. He is one of the lead delegates representing vivo in the 3GPP, holds numerous patents, and has chaired multiple 3GPP RAN1 sessions (which specify the physical layer of radio interfaces) that led to the successful standardization of MIMO, NR on unlicensed spectrum technologies. Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) is a key 5G technology that increases throughput and signal-to-noise ratio, while NR is a new radio interface and radio access technology for cellular networks. He has authored and contributed numerous technical papers on the subject of 3GPP RAN1 in 3G, 4G, and 5G standards.
“Brought to life by our strong R&D network across nine innovation centers and supported by research teams across the globe, vivo knows consumers best within the industry. We focus on innovations in hardware design and the software ecosystem to improve terminal performance and user experiences. Putting end users at the center of everything we do, vivo invests heavily into 5G connectivity to reach the stage of product realization and getting this technology into the hands of consumers,” he adds.
Vivo’s unique user-oriented innovation is the genesis behind its numerous patented contributions to 5G standards, many of which have been universally acclaimed at the 3GPP meeting and are currently already being adapted for everyday smartphone users.
One of vivo’s most notable contributions includes the standardization and performance enhancement of Rel-17 multi-SIM technology. Previously, an incoming voice call from one competing 5G SIM card would interrupt the data flow of the other, resulting in abysmal performance as one would cancel the other. Having discovered early on that consumers had a preference for 5G smartphones with dual-SIM card slots for greater flexibility in different usage scenarios, vivo researchers successfully sought to negate the clash, leading to the existence of multi-SIM 5G smartphones on the market today.
The initial implementation of 5G technology was initially found to be quite resource-draining compared to devices running on 4G. However, consumers had grown accustomed to the substantial usage time allowed by previous smartphones.
Always innovating with the user in mind, the Rel-16 terminal power-saving technology patented by vivo manages to simplify terminal actions. It lowers normal energy consumption by creating a new “dozing” state, allowing the device software to become inactive while the hardware becomes idle. 5G smartphones can now intelligently catch every chance to take a rest, thereby prolonging battery life.
Additionally, vivo underwent algorithm and system optimization to facilitate this technology, combined with 120-watt fast charging to ensure complete user satisfaction with their devices. Select vivo smartphones are housed with a superconducting carbon fiber liquid cooling system to prevent device overheating, which is especially prevalent during intensive multimedia entertainment or e-sports usage scenarios.
Another issue raised by 5G technology is the increasing number of antennas and components installed inside a smartphone. However, users are relentless in their pursuit for ultra-thin smartphones encased in sleek metallic exteriors. Never one to disappoint, vivo’s proprietary 3D stack design uniquely encases all of this industry-leading technology to allow new 5G smartphones to be even slimmer than its 4G predecessors.
As 5G commercial networks are gradually deployed around the world and progressively advanced devices increasingly permeate every aspect of our livelihoods, thought leaders of the mobile industry are already looking forward to its next generation: 6G.
Vivo is part of a select few that hold the extensive expertise and in-depth understanding of consumer needs in order to turn this vision into a reality. Along with leading companies, research groups, and academic institutions, this combined elite collective is expected to reach a consensus on the ideation and requirements for this future generation of connectivity. To kickstart this exciting new era, the vivo Communications Research Institute (VCRI) released two white papers in late 2020 that break down the facets of 6G technology. Providing a diverse set of hypothetical scenarios and case studies, vivo communication standard experts have analyzed how the sixth generation will embody much more than technological transformation as it merges our physical and digital worlds.
“Currently, mobile infrastructure is still relatively isolated from the physical world, existing solely as an auxiliary tool for consumer usage. An extreme degree of seamlessness will be required to dynamically connect our physical surrounding with the omnipresent digital systems. In 2030 and beyond, 6G standard technologies will begin to foster a ubiquitous, sophisticated, real-time, and fully integrated digital world. This new realm will revolutionize thousands of industries with an extraordinary variety of applications to result in an efficient, sustainable, and eco-friendly future world,” says Tamrakar.
6G communication systems will comprise many device terminals to realize the agile perception and accurate control between digital systems with our physical domain; this is comparable to the nerve endings that perceive essential information from every inch of the human body for our central nervous system to take responsive measures. As such, a large number of harmoniously connected and intelligent terminals in the form of smartphones or wearable devices will be fundamentally required in order for the entire IoE (internet-of-everything) system to be effective. To that end, vivo has launched a smartwatch, wireless earbuds, and Jovi AI assistant to introduce users to its own flourishing digital ecosystem.
Notwithstanding all of this exhaustive groundwork laid by technology companies, the 5G race and the 6G marathon are far from over. Nonetheless, affordable smartphones with innovative features will continue to act as the interface for everyday users to engage with the all-encompassing network infrastructure, to accelerate the impending intelligent transformation of society.
This content was produced by Insights, the custom content arm of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial staff.
[ad_2]